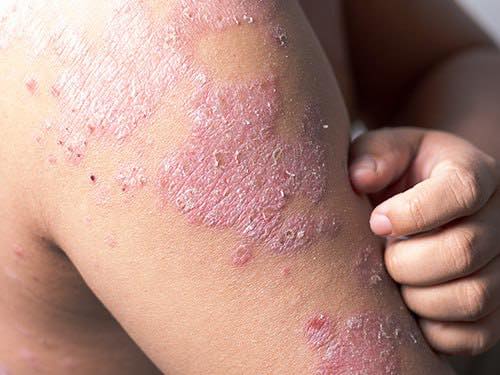
Eczema is a chronic (long-lasting)skin condition that comes with inflammatory symptoms.
It is not a specific condition, rather it’s a group of inflammatory conditions of the skin.
Eczema often have its onset in early childhood and can stick around into adulthood, but it doesn’t discriminate.
it can affect anyone at any age. It is known as Dermatitis, and the most common type is atopic dermatitis.
SYMPTOMS
The symptoms of Eczema are not specifically the same for different individuals and some of them include;
-Itchy skin usually intense
-Dry and cracked skin
-Skin discoloration that varies based on skin color
-Rashes that ooze appear raw when scratched
-Swollen or bumpy skin mostly on black skin
-Darkened skin around your eyes
-Thickened and scaly skin
CAUSES OF ECZEMA
The specific cause of eczema is not completely understood.
Exposure to certain skin irritants is a key factor, however, here are some implicated factors:
Immune System Overreaction: Eczema is often triggered by an overzealous immune system reacting to a weakened skin barrier.
It’s just like your skin’s defense system going into overdrive, and then cause inflammation and other symptoms.
-Filaggrin Deficiency: Another key factor is a protein called filaggrin.
This protein is more like the unsung hero of your skin, helping to keep it moisturized and healthy.
When there’s a deficiency in filaggrin, your skin struggles to maintain its barrier function, leading to dryness and making it more susceptible to irritants and allergens.
WHAT CAN TRIGGER ECZEMA?
-Sweating
-Changes in temperature
-Preservatives used in detergent and cleansing products
-Scented skin products
-Cigarette smoke
-Some synthetic fabrics
-Allergens such as; mold, pollens, animal dander
-Upper respiratory tract infection
-Stress
-Food allergies
Eczema is an unpleasant lifelong condition, but it has a mysterious view about it.
Between flare-ups, it can slip into remission, making symptoms vanish for a while, only to reappear unexpectedly later on.
Good news is that there are treatment options
📌 Let’s see below
TREATMENT
-Oral and topical steroidal medications
-Antihistamines for itching
-Immunosuppressants
-Phototherapy
Based on symptoms and severity, your doctor may use any of the approaches above or a combination of some of them.
PREVENTION
-Moisturize your skin at least twice daily
-Have proper bathing daily
-After bathing, gently pat your skin dry
Limit overexposure to heat
-Avoid harsh soaps that may rip off skin natural oil
-Change your choice of detergent if you experience irritations
-As much as you can, avoid all triggers and allergens
📌 Note
The goal of treating eczema isn’t to cure it, but to manage the symptoms, prevent flare-ups, avoid complications, and achieve long-term remission.
Rest assured, eczema itself is not contagious.
However, it is important to note that secondary infections, which can arise from inadequate treatment, might be contagious.
So, treat it promptly, practice good hygiene, and embrace healthy lifestyle changes.
Your skin will love you 🥰